By Patricia M. DeMarco, Ph.D.
May 1, 2022
Land Acknowledgment: I write from Pittsburgh, which occupies ancestral lands of the Haudenosaunee, Lenape, Osage, and Shawnee peoples.
For most of human history, people struggled to survive and thrive against the forces of nature, as is the case with most other species on the planet. Discovering and harnessing fossil resources to use as fuel released human civilization from the constraints of nature. The Industrial Revolution rested on coal, then petroleum to allow people to conquer seasonal weather challenges, nighttime darkness, travel and industrial operations beyond the scope of human or animal power and bio-based fuels such as wood and whale oil. Burning fossil fuels to support almost all human enterprises has now breached the limits of the natural ecosystems in which we live and upon which we depend for survival.[1]
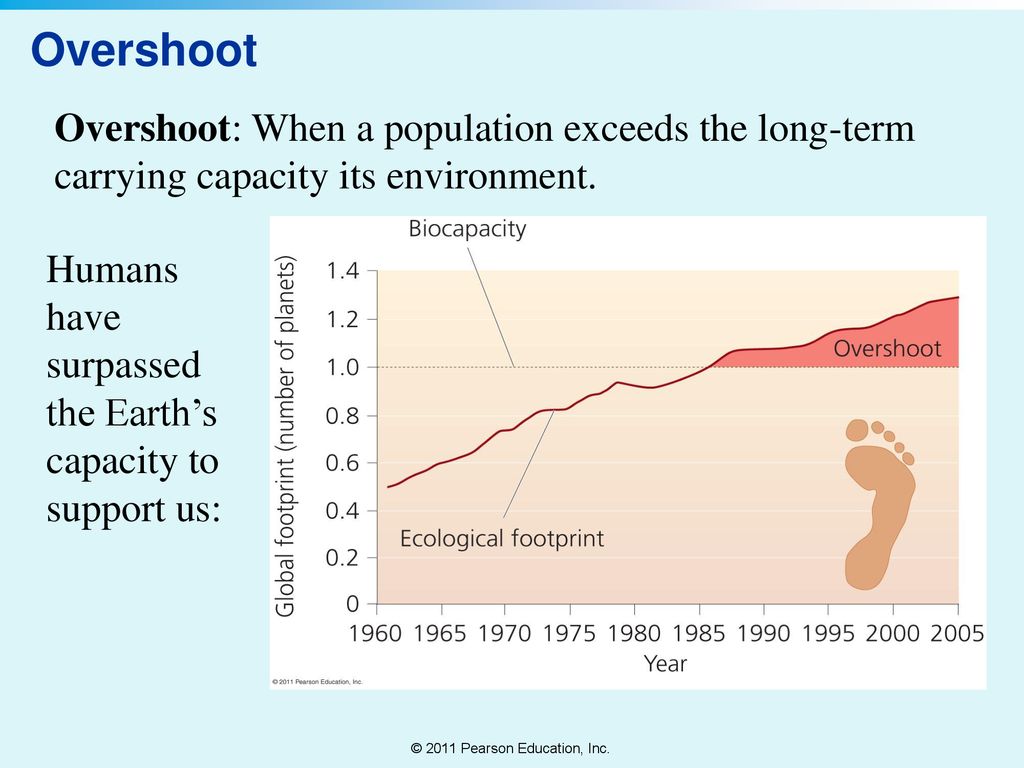
However, even as the calls of alarm for the rapid pace of global warming become more urgent, the Russian invasion of Ukraine has become the latest excuse to defer the energy system transformation to a renewable base. As noted by the Council on Foreign Relations:
The United States’ dependence on oil has long influenced its foreign policy. U.S. oil development spans three major periods: the rise of oil as a commodity, beginning in 1850; the post–World War II age of geopolitical competition; and the post–Cold War era of deregulation and diversification. Most recently, Russia’s war with Ukraine has aggravated geopolitical tensions and revived the debate about U.S. energy independence.[2]
Calls for relaxing restrictions on drilling and increasing production for export set back policy momentum for reaching the necessary reductions in greenhouse gas emissions. The increases in gasoline prices illustrate how interdependent the U.S. is on the global market which sets the price of petroleum. U.S. energy policy has long been driven by the concept of cheap gas at the pump. People have become accustomed to using the gas price as a barometer of our energy security. In fact, this is just another signal of our vulnerability.
Energy independence is a term of political manipulation with several definitions, all contested by economists and energy analysts. Those who define energy independence as exporting more than we import fail to acknowledge that even when exporting oil, the U.S. still imports oil.[3] In 2021, the United States exported about 8.63 million barrels per day (b/d) and imported about 8.47 million b/d of petroleum, making the United States an annual total petroleum net exporter for the second year in a row since at least 1949.[4]
As long as the U.S. participates in an international marketplace where the price of the commodity is determined by global geo-political forces, the concept of energy independence has no real meaning. Even renewable energy systems are interdependent in the global marketplace, as is evident in the arguments over tariffs on imports of solar panels from China[5], and the sourcing and trade of rare earth materials such as lithium.[6]

Rather than seek an unachievable goal of “energy independence,” we can seek to reduce our vulnerability. It is critical to recognize that failing to reduce greenhouse gas emissions from burning fossil fuels to zero, at least by 2050, will be catastrophic for our economy and for the viability of the planet.[7] The laws of Nature are NOT negotiable – the laws that support continued use of fossil fuels must change immediately.

Natural History Museum. Biodiversity Loss[8]
Technology is not a barrier to achieving 100% renewable energy system in the U.S. by 2050. A 2015 analysis conducted by researchers at Stanford University and the University of California at Berkeley found that 100% wind and solar power — in conjunction with energy efficiency, energy storage and other advances to complement renewables — could provide electricity to the continental U.S. more reliably than the current system by 2050, and at lower projected costs.[9]
The political will to move the legal and regulatory infrastructure to support this goal has not been mobilized, even though most Americans see climate change as an important issue. Three-quarters of Americans say that human activity, such as the burning of fossil fuels, contributes to climate change at least some, with 46% saying it contributes a great deal.[10]However, opinions are sharply divided on partisan lines. Democrats say human activity contributes a great deal to climate change (71%), while just 17% of Republicans say the same.[11] Major policy changes will be needed to achieve the necessary transformation of. Our energy system, but as the last session of Congress has illustrated, political conditions are unlikely to achieve the necessary level of action.
The complexity of climate change issues and the diversity of impact even within the U.S. complicates mobilization around climate action. A recent study by the Allegheny Conference Energy Task Force in Pittsburgh has chosen a middle of the road path, even though it recognizes that this approach will not meet the climate goal of limiting global warming to 1.5°C by 2050.[12] The principal focus area for funding identified in this report relies on continued production of natural gas from hydraulic fracturing to produce “blue hydrogen” as an industrial fuel source, and applying carbon capture and sequestration technologies to control emissions.[13] This approach locks in dependence on fossil fuels for another two or three decades.

People fear the loss of jobs in the energy sector, without recognizing that the skills and capabilities of workers in this sector are readily transferable to the clean energy economy. A federal investment package with annual average allocations of $11.3 billion to Pennsylvania, from 2021 to 2030, along with an additional $19.7 billion in private investments would generate approximately 243,000 jobs in Pennsylvania— enough to bring Pennsylvania’s high unemployment rate back down towards 4 percent.[14]
The burden of immediate action has fallen to local governments to act. At the local level, people see the immediate effects of climate change vulnerability. In coastal areas, local governments have to address higher tides and more severe storm surges which have been highly dramatized in the media coverage of hurricane damage. Usually there is little or no discussion of the connection of larger, more severe and longer lasting storm systems to global warming and its effects on storm formation. Inland areas see drought and flood damage as well as landslides and stormwater damage. Federal assistance only comes when disastrous levels of infrastructure damage occur, such as in Hurricane Katrina or Hurricane Sandy.
For the gradual increase of climate effects, local governments have been adopting climate action plans individually[15]and as regions.[16] In all cases, local climate action plans will require federal and state policy support by at least 2030 to support the goals established. For example, in the Forest Hills Climate Action Plan, the predominant sector is Residential. Shifting the heating systems of most houses from natural gas to high efficiency heat pumps will require policy support as well as financial assistance in the form of tax incentives or grants. Local governments have not organized well to pressure state and federal levels of government to respond to these needs.
Forest Hills Borough net zero energy -Volpatt photo
The assumption that reducing energy consumption cuts economic productivity was reinforced by the COVID-19 pandemic. Energy consumption did fall as pandemic restrictions limited travel and other activities.[17] However, decoupling energy use from the economic productivity has occurred in many countries already. It is certainly plausible to decouple primary energy consumption growth from meeting the planet’s energy needs. For example, Denmark has 30 years of proven history in reducing the energy intensity of its economy.[18]
It is important to recognize that we need to make a transformation of the energy system, not simply substitute renewable fuels for fossil fuels. The entire approach changes when we focus on supplying the work necessary to meet the needs for people, agriculture, and industry in a different way. There are at least three points here:
- primary energy consumption automatically goes down when switching from fossil fuels to wind, solar and hydroelectricity, because they have no conversion losses according to the usual definition of primary energy;
- living standards can be maintained while increasing energy efficiency;
- renewables-based systems avoid the significant energy usage of mining, transporting and refining fossil fuels and uranium.[19]
Ultimately, reducing our vulnerability to energy disruptions comes down to building energy systems that are in harmony with the laws of nature. We must change the dynamic of the conversation about climate change. It is critical for the survival of our planet and for the immediate well-being of every person to move rapidly to a sustainable energy system.
It is time to recognize the reality of our interdependence as human species to preserve the biodiversity of the planet and to restore the health of the ecosystems we depend on for our survival. Fresh water, clean air, and fertile ground support life on Earth as we know it. If we continue on this path, driven by greed and adherence to a fossil fueled economy, we will destroy ourselves, and all of the living Earth. I close with this reflection from Rachel Carson:
Mankind has gone very far into an artificial world of his own creation. He has sought to insulate himself, with steel and concrete, from the realities of earth and water. Perhaps he is intoxicated with his own power, as he goes farther and farther into experiments for the destruction of himself and his world. For this unhappy trend there is no single remedy – no panacea. But I believe that the more clearly we can focus our attention on the wonders and realities of the universe about us, the less taste we shall have for destruction.[20]

Citations
[1] IPCC, 2021: Summary for Policymakers. In: Climate Change 2021: The Physical Science Basis. Contribution of Working Group I to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [Masson- Delmotte, V., P. Zhai, A. Pirani, S.L. Connors, C. Péan, S. Berger, N. Caud, Y. Chen, L. Goldfarb, M.I. Gomis, M. Huang, K. Leitzell, E. Lonnoy, J.B.R. Matthews, T.K. Maycock, T. Waterfield, O. Yelekçi, R. Yu, and B. Zhou (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press.
[2] Council on Foreign Relations. Oil Dependence and U.S. Foreign Relations- Timeline 1850 -2022. April 2022. https://www.cfr.org/timeline/oil-dependence-and-us-foreign-policy
[3] Robert Rapier. “What Is Energy Independence?” Forbes. March 9, 2022. https://www.forbes.com/sites/rrapier/2022/03/09/what-is-energy-independence/?sh=29f94867730a
[4] U.S. Energy Information Administration. Petroleum and Other Liquids. U.S. Net Imports of Crude Oil and Petroleum Products 1975-2021 https://www.eia.gov/dnav/pet/hist/LeafHandler.ashx?n=pet&s=mttntus2&f=a
[5] David Stanway. “China says U.S. tariff extension on solar products hurts new energy trade.” Reuters February 7, 2022. https://www.reuters.com/business/energy/china-says-us-tariff-extension-solar-products-hurts-new-energy-trade-2022-02-05/
[6] Gregory M. LaRocca. “Global Value Chains: Lithium in Lithium-ion Batteries for Electric Vehicles.” U.S. International trade Commission, Office of Industries Working Paper No. 069. July 2020. https://www.usitc.gov/publications/332/working_papers/no_id_069_gvc_lithium-ion_batteries_electric_vehicles_final_compliant.pdf
[7] IPCC, 2022: Summary for Policymakers [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, M. Tignor, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem (eds.)]. In: Climate Change 2022: Impacts, Adaptation, and Vulnerability. Contribution of Working Group II to the Sixth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change [H.-O. Pörtner, D.C. Roberts, M. Tignor, E.S. Poloczanska, K. Mintenbeck, A. Alegría, M. Craig, S. Langsdorf, S. Löschke, V. Möller, A. Okem, B. Rama (eds.)]. Cambridge University Press. In Press. https://www.ipcc.ch/report/ar6/wg2/
[8] Yvonne DaSilve. Major study shows biodiversity losses can be reversed. Natural History Museum https://www.nhm.ac.uk/discover/news/2015/april/major-study-shows-biodiversity-losses-can-be-reversed.htmlYvonne
[9] Mark Z. Jacobson, Mark A. Delucchi, Mary A. Camerona and Bethany A. Frew. “Low-cost solution to the grid reliability problem with 100% penetration of intermittent wind, water, and solar for all purposes.” PNAS. December 8, 2015. vol. 112 no. 49 www.pnas.org/cgi/doi/10.1073/pnas.1510028112
[10] Alec Tyson, Cary Funk and Brian Kennedy. “Americans Largely Favor U.S. Taking Steps to Become Carbon Neutral by 2050.” Pew Research Center.March 1, 2022. https://www.pewresearch.org/science/2022/03/01/americans-largely-favor-u-s-taking-steps-to-become-carbon-neutral-by-2050/
[11] Katherine Schaeffer. “For Earth Day, key facts about Americans’ view of climate change and renewable energy.” Pew Research Center. April 22, 2022. https://www.pewresearch.org/fact-tank/2022/04/22/for-earth-day-key-facts-about-americans-views-of-climate-change-and-renewable-energy/
[12] Allegheny Conference Energy Task Force. “Our Region’s Energy Future – A strategy for accelerating decarbonization, investment and inclusive growth in the Pittsburgh region.” April 2022. https://www.alleghenyconference.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/2022_EnergyReport_D.pdf
[13] Ibid. Page 12. https://www.alleghenyconference.org/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/2022_EnergyReport_D.pdf
[14] Robert Pollin, Jeannette Wicks-Lin, Shouvik Chakraborty and Gregor Semieniuk. Impacts of the ReImagine Appalachia & Clean Energy Transition Programs for Pennsylvania – Job Creation, Economic Recovery, and Long-term Sustainability. University of Massachusetts Amherst, Political Economy Research Institute. January 2021. https://reimagineappalachia.org/wp-content/uploads/2021/01/Pollin-et-al-PA-Final-Report-1-22-21.pdf
[15] Borough of Forest Hills Climate Action Plan. December 16, 2020. https://files.dep.state.pa.us/Energy/Office%20of%20Energy%20and%20Technology/OETDPortalFiles/ClimateChange/Local_Climate_Action/Final_Forest_Hills_Climate_Action_Plan-12-17-2020.pdf
[16] Congress of Neighboring Communities. Infrastructure and Utilities Coordination Working Group. CONNECT Climate Action Plan. May 2022 (In Press) https://www.connect.pitt.edu/working-groups/infrastructure-utilities-coordination-working-group
[17] Peng Jiang, Yee Van Fan and Jiri Jaromir Klemes. “Impacts of COVID-19 on energy demand and consumption: lessons and emerging opportunities.” Applied Energy. March 1, 2021. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7834155/#__ffn_sectitle
[18] T.W.Brown, T.Bischof-Niemz, K.Blok, C.Breyer, H.Lund, B.V.Mathiesen . Response to ‘Burden of proof: A comprehensive review of the feasibility of 100% renewable-electricity systems.’ Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. Volume 92, September 2018, Pages 834-847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.04.113 See also article to which this response is directed:https://www.utilitydive.com/news/why-100-renewables-isnt-feasible-by-2050/560918/
[19] T.W.Brown, T.Bischof-Niemz, K.Blok, C.Breyer, H.Lund, B.V.Mathiesen . Response to ‘Burden of proof: A comprehensive review of the feasibility of 100% renewable-electricity systems.’ Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. Volume 92, September 2018, Pages 834-847. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.04.113 See also article to which this response is directed:https://www.utilitydive.com/news/why-100-renewables-isnt-feasible-by-2050/560918/
[20] Rachel L. Carson. “The Real World Around Us.” In Linda J. Lear (Ed.) Lost Woods – The Discovered Writing of Rachel Carson. Beacon Press. Boston 1998. Page 163.


